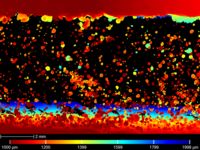
HIC TESTING IN ACCORDANCE WITH NACE TM 0284
HIC = hydrogen-induced cracking
Aim:
The HIC test is used to test pipeline and pressure vessel steels, especially plates and pipes, for their resistance to sour gas (natural gas containing H2S).
Mechanism:
Within the metallic matrix of steels there are defects in which cracks can develop further through the H2S corrosion process. This damage mechanism is promoted in a sour gas environment and is not easy to detect. Severe environmental damage and personal injury can be the results of the choice of a material that is not suited for the application.
Procedure for HIC testing:
Samples of 100 mm x 20 mm x wall thickness are taken from the material, pipes or plates to be tested and immersed for 96 hours into a solution of common salt and acetic acid that has been saturated with H2S. Afterwards, the specimens are tested metallographically for the formation of cracks that had been induced by hydrogen.
RIO GmbH is listed by Saudi Aramco and also carries out HIC testing in accordance with 01-SAMSS-016, 01-SAMSS-035, 01-SAMSS-043 and SAF 175-IR010210.
SSC TESTING IN ACCORDANCE WITH NACE TM 0177
In high-strength steels cracks can arise in the zone that had been affected by heat in weld seams due to the action of mechanical stress in atmospheres containing hydrogen sulphide. The testing of materials with regard to this damage mechanism, "Sulphide Stress Cracking“ (SSC) is done in accordance with NACE TM 0177. The parameters for this kind of testing are test duration and tensile stress to be applied.